Kerf, a security-log visualization tool (2003-2005)
This project is no longer active; this page is no longer updated.
Related keywords:
[security]
Summary
The text on this page was written contemporaneous to the
project.
Kerf (formerly known as Sawmill) is a set of tools designed to help
system administrators analyze intrusions in their network of
workstations. Our tools collect host and network log data in secure
databases, allow administrators sophisticated searches using our
SQL-language variant (SawQL, pronounced saw-kwill), and present the
results through a browsable graphical interface. We view the SawQL
inquiry as a representation of the sysadmin's hypothesis about the
intrusion; our tools interactively refine that hypothesis to a more
precise picture of the attack. All results may be recorded for future
reference or referral to authorities.
Project Goals
Given:
- An intrusion, of some kind, has been detected
- Network logs and host logs capture activity
Answer questions:
- How did the hacker get in?
- What did the hacker do then?
- Where did the hacker come from?
More Specifically:
- Identify the characteristics of an attack using host and network sensors
- Develop a hypothesis about the nature and origin of the attack
- Share the hypothesis with security managers at other sites
- Archive the data for use as evidence in law-enforcement actions
Research Outcome
New Intrusion Analysis Tools
- Expect and encourage interaction
- Human administrator forms a hypothesis
- Tool helps to gather information
- Expect and encourage iteration
- Tool helps administrator to refine hypothesis
- Expect and encourage collaboration
- Tool helps administrator to communicate hypothesis to other administrators
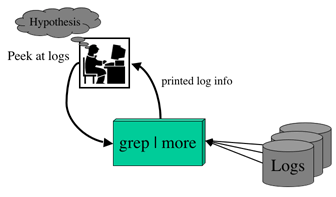
Old Process
Iterative hypothesis refinement
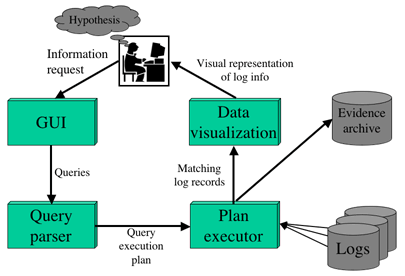
New Process
Iterative hypothesis refinement
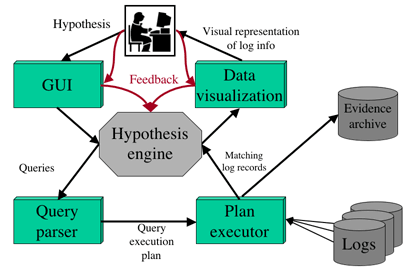
Automated hypothesis refinement
Unique Contributions and Deliverables
- New paradigm for intrusion analysis: hypothesis generation and refinement
- New tools for hypothesis generation and refinement
- New algorithms and tools for distributed log correlation
- New visualization methods for large log data sets for intrusion analysis
Relevance (Government and Industry)
- There are many hackers that attack computers
- Attacks disrupt operations
- Attackers may access sensitive data
- Hackers are creative and invent new ways
- Current IDSs do not detect new attacks
- We propose tools for intrusion analysis with the human in the loop via hypothesis refinement
Relationship with other projects
Intrusion detection systems
- Our project is focused on intrusion analysis rather than intrusion detection
- Examples of IDS: Stanford’s EMERALD (funded by DARPA) and UCSB’s STAT
- We use security services provided by IDS
- As provider of events that trigger analysis
- As data to be analyzed
Internet Detection Working Group of Internet Engineering Task Force
- IDWG of IETF
- Standards for Intrusion Detection Systems
- A new interchange format: IDMEF
- A new interchange protocol: IDXP
- We plan to support IDMEF input.
MIT Lincoln Labs
- A testbed for comparing IDSs
- We can use their test scenarios as test cases for input to our analysis system
NIST
- NIST MAIDS:
- Using mobile agents in an IDS
- We may use mobile code to collect log data
- Common Criteria Evaluation Scheme
- They evaluate IDS and other security tools
- A common set of standards for those tools
- Federal Computer Incident Response Center
- FedCIRC
- A web site for reporting incidents, sharing information
- Not an automated tool for hypothesis sharing
CERT
- AirCERT
- Real-time collection of intrusion information from sensors around the country
- Collected in CERT KnowledgeBase for analysis
- ACID (Analysis Console for Intrusion Databases)
- A GUI interface to database of log/event data
- “Export to email” for informal collaboration
- No hypothesis generation, refinement, or sharing
Summary
- Our project is intrusion analysis, not intrusion detection
- Our tools complement existing technology and can use IDS alerts as input
- Our tools are unique and can help to form, refine, and share hypotheses
- Our tools will help system administrators and law enforcement with real problems
Talk slides
- Title: Sawmill: Infrastructure for Distributed Collaboration in Detecting Network Attacks
Authors: Javed Aslam, David Kotz, Daniela Rus
Date: Jan. 2002
Download: PowerPoint
- Title: Sawmill: Infrastructure for Distributed Collaboration in Detecting Network Attacks
Authors: Javed Aslam, David Kotz, Daniela Rus
Date: Feb. 2002
Download: PowerPoint
- Title: Log-based Analyses for Decentralized Attack Detection
Authors: Marco Cremonini, Andrea Schiavoni
Date: Sep. 2001
Download: PowerPoint
People
Jay Aslam, Sergey Bratus, Marco Cremonini, David Kotz, Kevin
Mitcham, Ron Peterson, Daniela Rus, Brett Tofel, and students Kyle
Smith, Virgil Pavlu, and Wei Zhang.
Funding and acknowledgements
The Kerf project was supported by
Dartmouth's Institute for Security Technology Studies
(ISTS)
with funds from
the US Department of Homeland Security (Office for Domestic Preparedness),
under award number 2000-DT-CX-K001.
The views and conclusions contained on this site and in its documents
are those of the authors and should not be interpreted as necessarily
representing the official position or policies, either expressed or
implied, of the sponsor(s). Any mention of specific companies or
products does not imply any endorsement by the authors or by the
sponsor(s).
Papers (tagged 'kerf')
[Also available in BibTeX]
Papers are listed in reverse-chronological order;
click an entry to pop up the abstract.
For full information and pdf, please click Details link.
Follow updates with RSS.

- 2005:
-
Javed Aslam, Sergey Bratus, David Kotz, Ronald Peterson, and Daniela Rus.
The Kerf toolkit for intrusion analysis.
IAnewsletter.
Summer 2005.
[Details]
- 2004:
-
Javed Aslam, Sergey Bratus, David Kotz, Ron Peterson, Daniela Rus, and Brett Tofel.
The Kerf toolkit for intrusion analysis.
IEEE Security and Privacy.
November 2004.
[Details]
We consider the problem of intrusion analysis and present the Kerf Toolkit, whose purpose is to provide an efficient and flexible infrastructure for the analysis of attacks. The Kerf Toolkit includes a mechanism for securely recording host and network logging information for a network of workstations, a domain-specific language for querying this stored data, and an interface for viewing the results of such a query, providing feedback on these results, and generating new queries in an iterative fashion. We describe the architecture of Kerf, present examples to demonstrate the power of our query language, and discuss the performance of our implementation of this system.
Javed Aslam, Sergey Bratus, David Kotz, Ron Peterson, and Daniela Rus.
Kerf: Machine Learning to Aid Intrusion Analysts.
Proceedings of the USENIX Security Symposium.
August 2004.
Work-in-progress report.
[Details]
Javed Aslam, Sergey Bratus, David Kotz, Ron Peterson, Daniela Rus, and Brett Tofel.
The Kerf toolkit for intrusion analysis.
Technical Report, March 2004.
[Details]
We consider the problem of intrusion analysis and present the Kerf Toolkit, whose purpose is to provide an efficient and flexible infrastructure for the analysis of attacks. The Kerf Toolkit includes a mechanism for securely recording host and network logging information for a network of workstations, a domain-specific language for querying this stored data, and an interface for viewing the results of such a query, providing feedback on these results, and generating new queries in an iterative fashion. We describe the architecture of Kerf, present examples to demonstrate the power of our query language, and discuss the performance of our implementation of this system.
- 2003:
-
Javed Aslam, Sergey Bratus, David Kotz, Ron Peterson, Daniela Rus, and Brett Tofel.
The Kerf toolkit for intrusion analysis (Poster abstract).
Proceedings of the IEEE Workshop on Information Assurance.
June 2003.
[Details]
We consider the problem of intrusion analysis and present the Kerf toolkit, whose purpose is to provide an efficient and flexible infrastructure for the analysis of attacks. The Kerf toolkit includes a mechanism for securely recording host and network logging information for a network of workstations, a domain-specific language for querying this stored data, and an interface for viewing the results of such a query, providing feedback on these results, and generating new queries in an iterative fashion. We describe the architecture of Kerf in detail, present examples to demonstrate the power of our query language, and discuss the performance of our implementation of this system.
[Kotz research]




